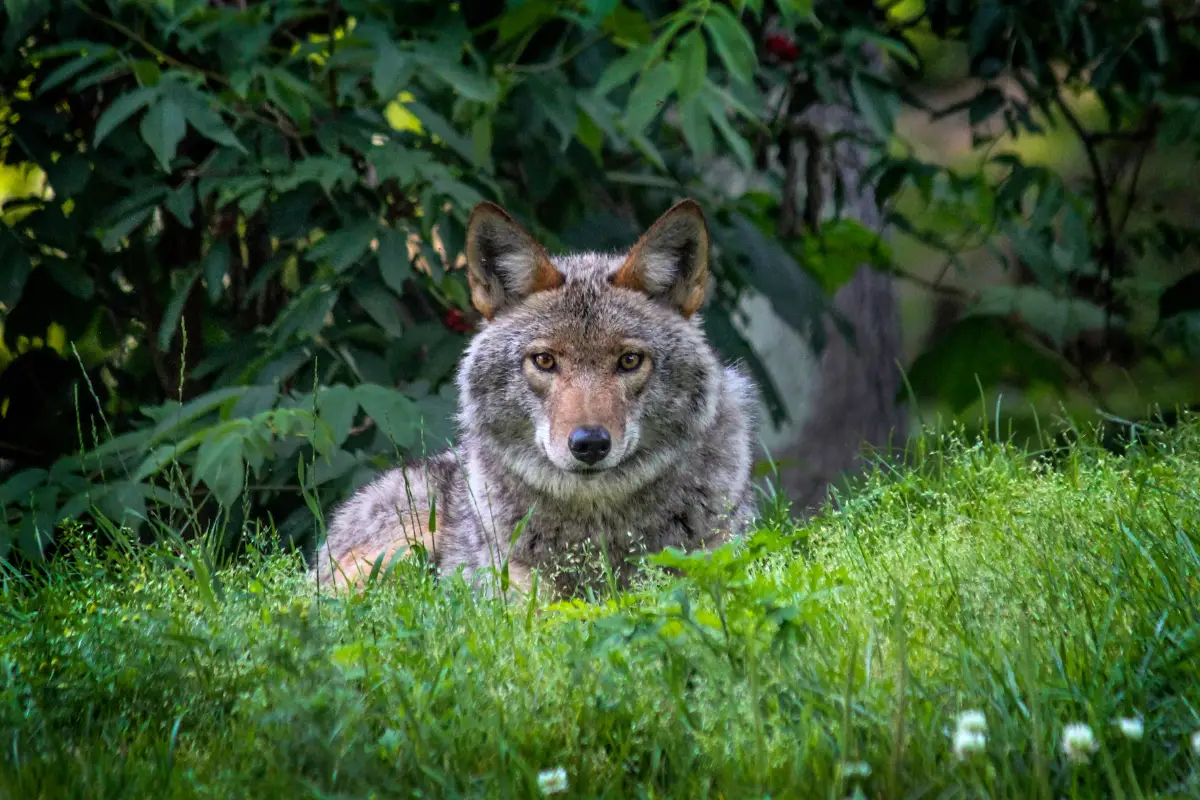
Coyotes (Canis latrans) are generally thought of as plains animals but their extreme adaptability has led them to inhabit much of North and Central America.
Coyote Habitat
Coyote habitats include prairies, and deserts, and recently (within the past one hundred years or so) it has expanded to cover forests, mountains, swamps, tundra, and temperate rainforests. Coyotes have even adapted to urban and suburban environments.
Coyotes can be diurnal, crepuscular, or nocturnal. Though primarily nocturnal, they have been able to adapt their circadian rhythm to suit that of their most abundant prey. This is the same factor that determines their most suitable habitat.
One of the most important things that coyotes look for in suitable habitats, along with abundant prey, is cover. While they only use dens while rearing pups their home range will include worthy sites for their dens, as well as other forms of brush and cover.
Crafty, intelligent, and stealthy, coyotes can thrive in a great number of ecosystems and environments. Thanks to the near eradication of its natural predators, they have gone from being located mostly in the southwestern United States to finding livable habitats anywhere from southern Alaska to southern Mexico and Panama.
However, their greatest numbers are in the southern plains and the Sonoran Desert regions.
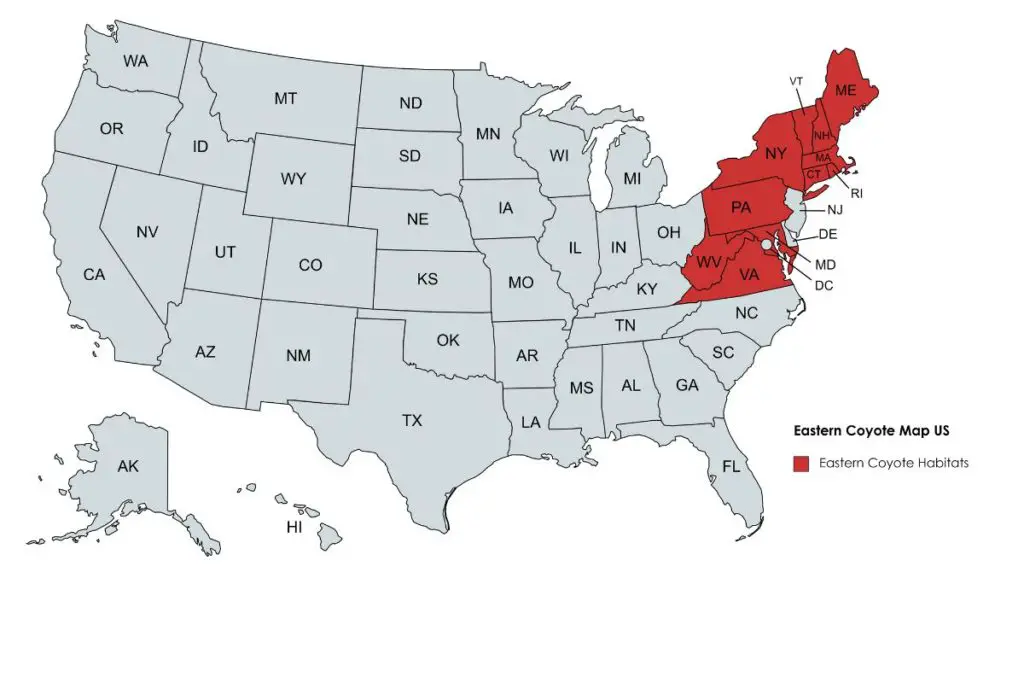
Eastern Coyote Habitat
One of the nineteen subspecies of this animal is the eastern coyote. DNA evidence shows that the eastern coyote (Canis latrans thamnos) is not the same as the “coywolf” which would be equal parts wolf and coyote. Instead, these animals are descendants of the Great Plains coyotes that have picked up percentages of the gray wolf, eastern wolf, and domestic dog.
Historically, the easternmost boundary of the coyote’s habitat range was the Appalachian Mountains. With the near extirpation of the wolf in the contiguous United States and southern Canada, coyotes started expanding their territories east. Along the way, they encountered remnants of the wolf population and through occasional crossbreeding, the eastern coyote was born.
Eastern coyotes can be found in New England, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, Virginia, and Washington, D.C.
They can also be found in Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia. They have even been found as far east as Newfoundland and Labrador.
Desert Coyote Habitat
A skilled hunter and opportunist, this omnivore will eat almost anything. Coyotes can be found in all of the desert areas of north and central America, and they choose their habitat locations wisely, based on local food and water sources, as well as other factors.
Coyotes are most populous in the large Sonoran Desert thanks to its subtropical warmth in the winter and two rainy seasons, along with it being the most biologically diverse desert in the world.
While coyotes are new to the eastern United States, they are not new to the desert. Canis latrans mearnsi, or Mearns coyote, can be found in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Sonora, and Chihuahua. While the color of their fur can vary, desert coyotes will usually display a desert yellow color.
Mountain Coyote Habitat
Canis latrans lestes or Mountain coyotes can be found in sub-alpine forests, alpine meadows, and ponderosa pine forests. Thanks to the extirpation of wolves and cougars, this subspecies of the coyote have found a new home in the mountainous regions of western Canada and the United States.
Forest edges and meadows, along with areas that have been cleared and developed for agricultural use, areas cleared by fires, and areas cleared by logging make excellent habitat locations for coyotes. These areas usually provide an abundant food source.
The mountain coyote, also known as the Great Basin coyote, can be found in British Columbia, Alberta, Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, California, Nevada, Colorado, and New Mexico.
Coyote Original Habitat
The coyote is also known as the prairie wolf and, historically, was most common on the Great Plains of North America. Archaeological evidence has revealed that the species roamed the eastern part of the continent as well, but disappeared from there towards the end of the last glacial period, around 12,000 years ago.
Before the arrival of European settlers, coyotes thrived in the grasslands and sparsely wooded areas of the southwestern United States. They also flourished in the shortgrass-steppe, semiarid sagebrush grasslands, and deserts. Today they can be found in virtually any type of habitat from arctic to tropical including swamps, tundra, dense forest, and suburban areas.
Their dispersal is largely due to two factors. The removal of its natural predators and modification of the landscape by humans. Their greatest numbers are still in the Great Plains states of the United States.
Although many people consider coyotes to be a nuisance, they play a vital (and positive) role in the environment. Source.
Coyote Diet and Habitat
Coyotes are mostly carnivorous and prefer fresh meat but will scavenge when the opportunity presents itself. Coyotes can be picky hunters with animals such as shrews, moles, and brown rats.
While coyotes can find suitable habitat locations in several different climates and ecosystems, they do show some preference. In the intermountain region of eastern Nevada, they prefer black sagebrush flats with high densities of black-tailed jackrabbits, to other habitat locations nearby.
Coyotes usually hunt individually or in pairs, however, they have been known to hunt in packs. The average distance covered in a hunting trip is usually around 4 kilometers or 2-3 miles, and their home range varies from 1,500 acres to 6,500 acres (10 square miles) or more.
The more food sources a habitat can provide, the greater the population of coyotes that will be found there. Food, as well as water, is one of the most important aspects of habitat, and survival.
However, coyotes are also very adaptable and opportunistic. So they have been known to push into areas that once were not suitable for the kinds of conditions they are used to. Despite these types of challenges, they still find cover, food, and shelter. Source.
See our article for How Long Do Coyotes Live?
Related Questions
Where do coyotes hide during the day?
Because coyotes are mostly nocturnal, they tend to hide or sleep during the daytime. You can find them hiding in the brush, in dens, and in locations with very little human activity.
Do coyotes live in the city?
There have been reports of urban coyotes. However, if they do live near a city, they are more likely to live in the rural outskirts, or areas with large plots of undisturbed land, vacant lots, and other places they can avoid humans.
- Hero Farm Dog Survives Epic Battle with Coyote Pack - December 9, 2024
- The 10-Minute Bedtime Routine That Changed My Dog’s Sleep Forever - November 29, 2024
- Creating a Safe Space for Nervous Pets: Your Guide to Pet-Friendly Havens - November 25, 2024

